Age-related macular degeneration (AMD)

Also called macular degeneration, AMD causes damage to the macula, the part of the eye needed for sharp, central vision, meaning the ability to view objects that are straight ahead. Central vision is needed for seeing objects clearly and for doing such common activities as driving, reading, writing, cooking, dialing a phone and recognizing faces. AMD can occur in one or both eyes, and it usually does not affect peripheral (side) vision.
Symptoms
The eye disorder is more common among people as they get older. AMD typically develops gradually and isn’t painful, so early symptoms can be mistaken for normal age-related vision changes. In other people, the disease progresses more quickly, and may lead to vision loss in one or both eyes.
Diagnosis
AMD may be suspected in people over 60 who experience recent changes in the center of their field of vision.

Visual Acuity Test
This test assesses clarity and sharpness of your vision. Each eye will be tested individually to check the ability of the eye to see letters of different sizes placed at a distance.
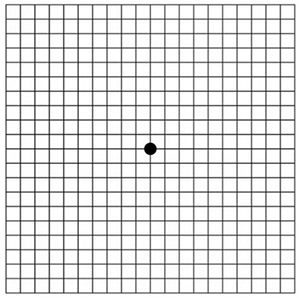
Amsler grid
People are asked to look at this grid, which resembles a checkerboard with a black dot in the center. This grid can test for defects in a person's central vision. If straight lines in the grid appear wavy or some lines appear to be missing, AMD is more likely.
Read More
Optical Coherence Tomography
OCT is a commonly performed diagnostic test to identify retinal diseases, such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD) or diabetic retinopathy.
Read More
Dilated Eye Exam
The pupils are dilated with eye drops so that the optic nerve and retina, located in the back of the eye, can be examined for signs of AMD. A special magnifying lens is used to perform this eye exam, during which an eye doctor is looking for fluid or blood or a mottled appearance in the macula.
Treatments
There are 2 types of AMD and treatment varies as per the type.

Dry AMD
Anti-biotic Eye drops and oral medication will help with the drainage of fluids or reduce the production of fluids itself, by lowering eye pressure. It is imperative to know the patient’s medical history and their conditions like allergies to take eye drops.
Wet AMD
The main treatment for wet AMD is the injection of medications called anti-VEGF agents. VEGF stands for vascular endothelial growth factor. A high level of VEGF in the eye is linked to the formation of the abnormal blood vessels that cause much of the damage in wet AMD. Anti-VEGF agents are used to combat the disease process and reduce the damaging effects of these leaky abnormal blood vessels. They are also able to effectively stabilize vision in many patients.
Clearer Vision is Just a Click Away!
Get yourself cared by the most experienced specialists

